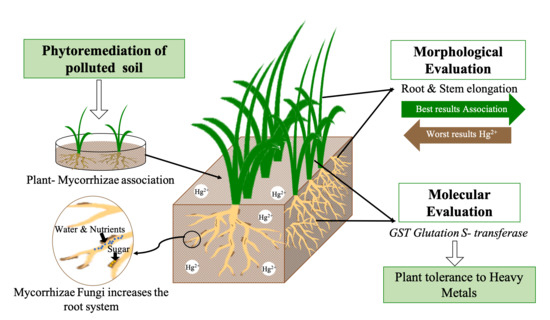
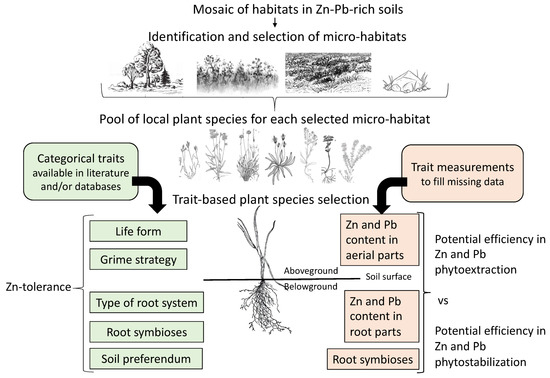
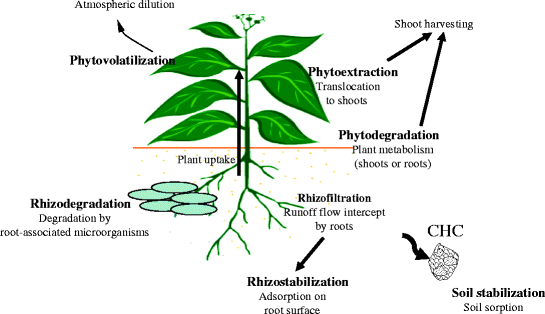
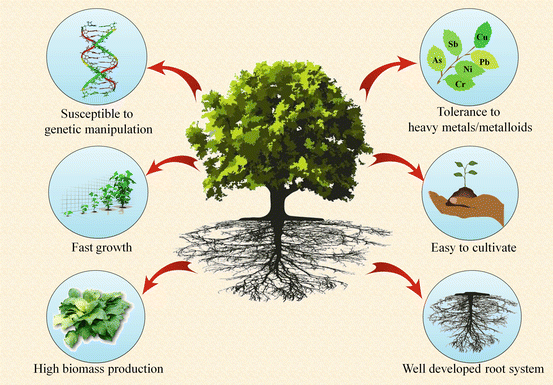
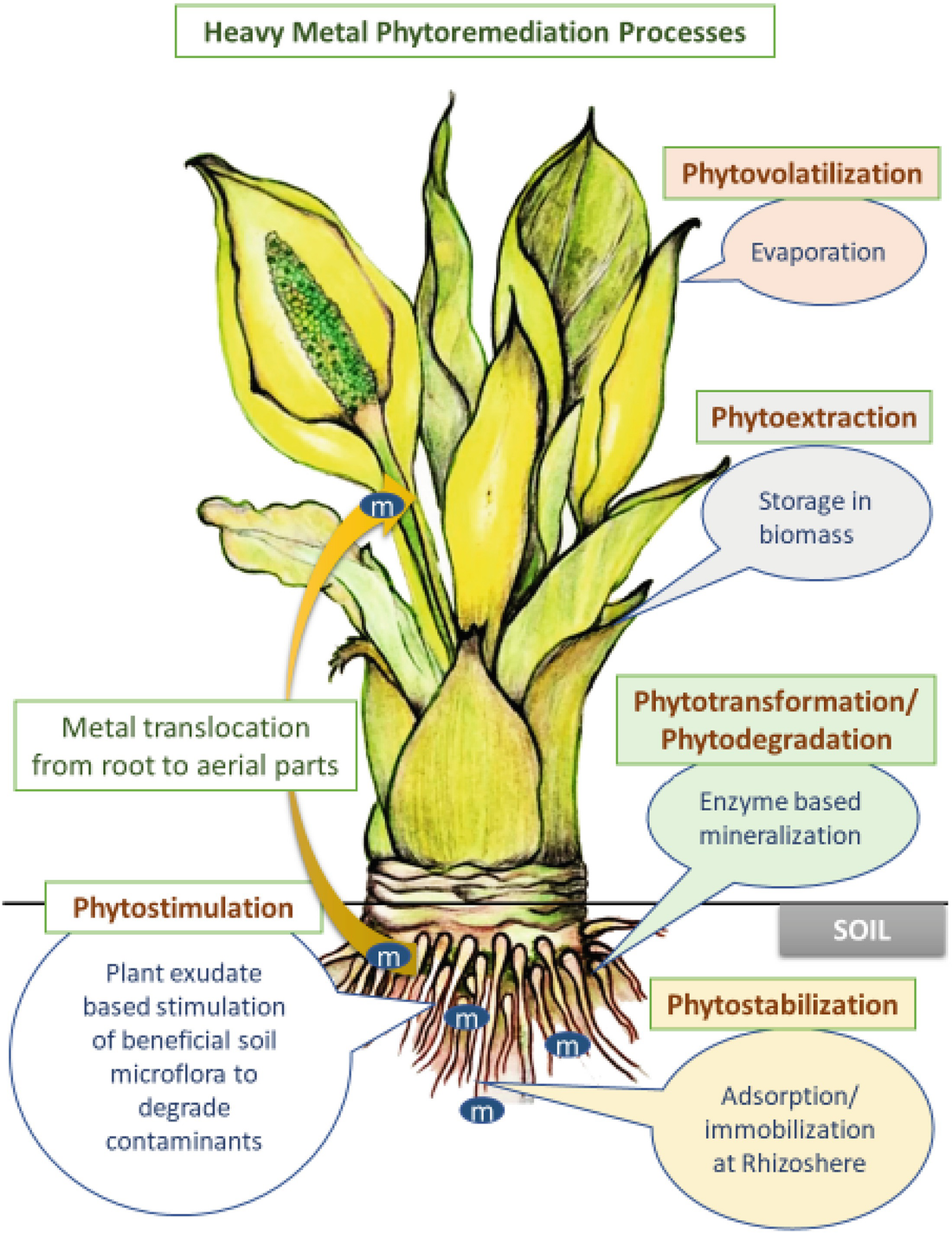
There are different types of phytoremediation mechanisms that are used to eliminate or degrade contaminants from soil and water discussed as.
Phytoremediation and root zone cleaning system.
Gies that might more efficiently clean up these sites.
Also phytoremediation is a slow process and a contaminated site needs to be large enough to grow enough plants.
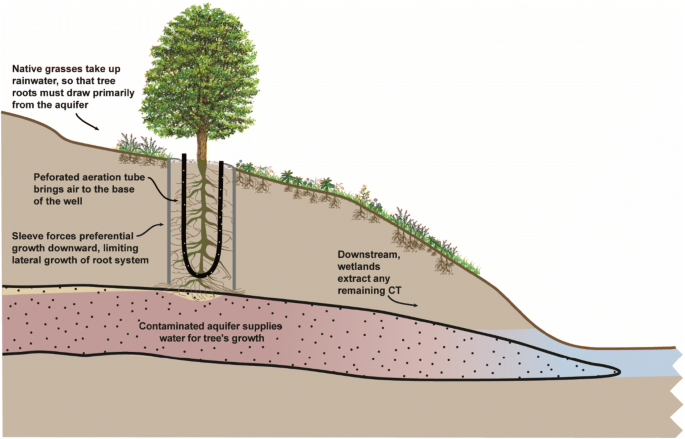
2 expiration is often not optimal because of less effective groundwater extraction through the tree root system.
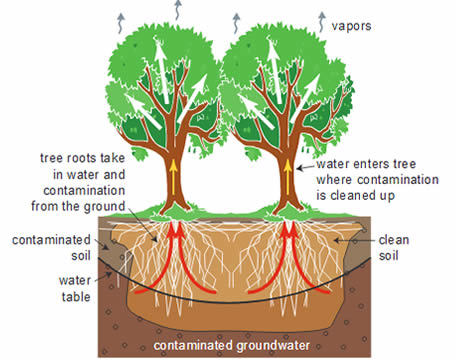
Phytoremediation is being increasingly used for example it has been employed in cleaning up of the contaminated groundwater site at aberdeen proving ground in maryland near a disposal site.
Phytoremediation can be used to clean up organic contaminants from surface water ground water leachate and municipal and industrial wastewater.
Phytoremediation is however limited to the root zone of.
And 3 the need to.
As a cleanup system at a site with zinc contamination in the root zone of some of the trees.
It is a compilation of.
However phytoremediation suffers several limitations.
The contaminating material should always be present within the root zone of the plants to make it accessible to the roots.
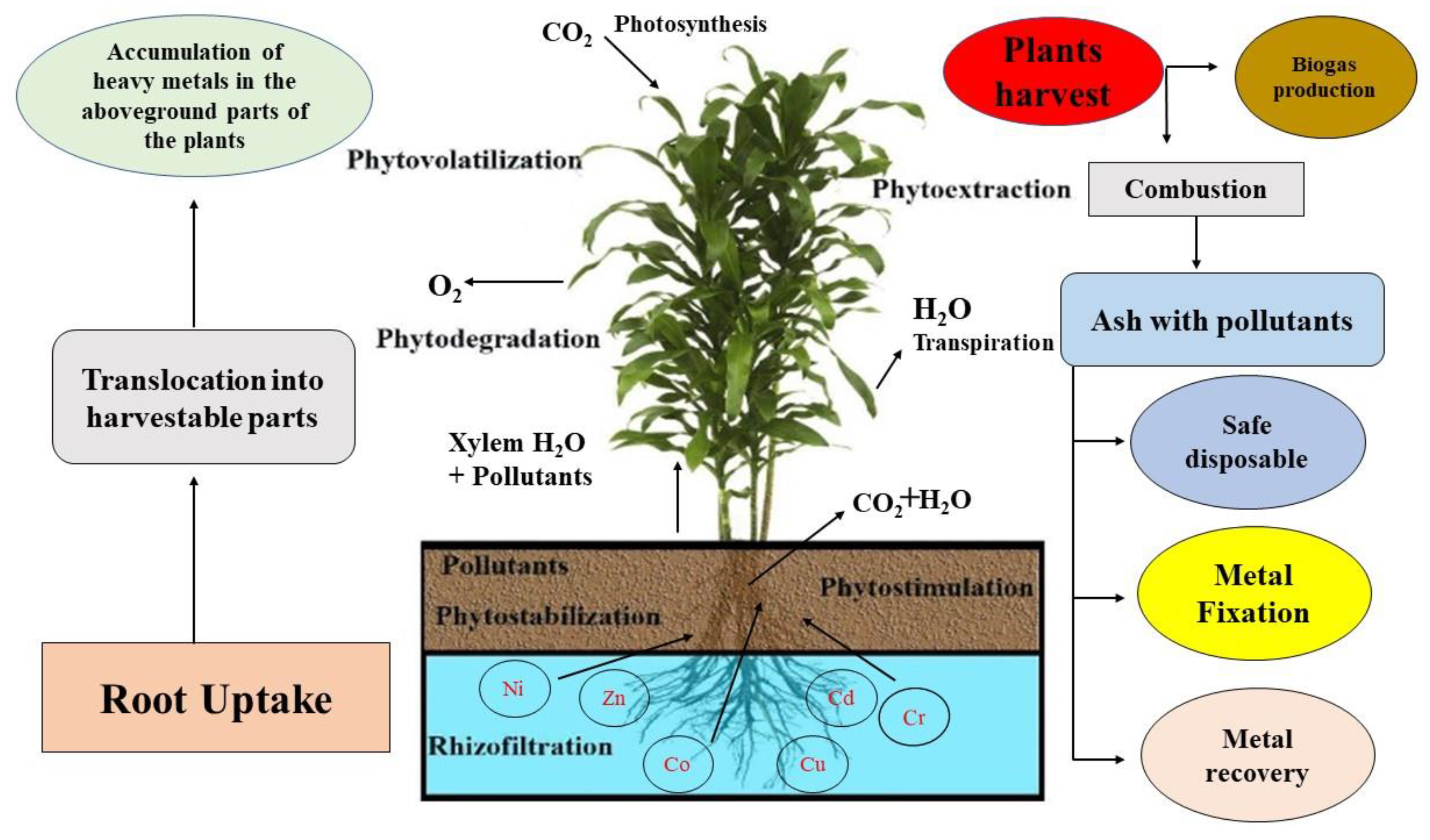
Classification of phytoremediation on the basis of mechanisms.
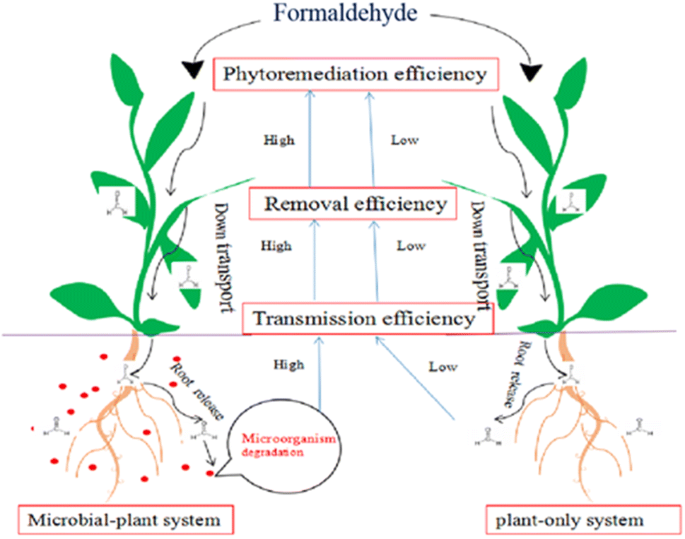
Plants also produce enzymes such as dehalogenase and oxygenase which help catalyze degradation.
This document defines terms and provides a framework to understand phytoremediation applications.
References and recommended reading greipsson s.
The plants used in phytoremediation are generally selected on the basis of their growth rate and biomass their ability to tolerate and accumulate contaminants the depth of their root zone and their potential to transpire groundwater.
Phytoremediation of contaminated sites should ideally not exceed one decade to reach acceptable levels of contaminants in the environment.
Phytoremediation is a bioremediation process that employs varieties of plants to eliminate transfer maintain extract or degrade contaminants in the soil and groundwater.
Once the reed plants create an established stand usually after the first growing season the reed bed requires little or no maintenance.
This site was heavily contaminated due to the burning and disposal of warfare and industrial chemicals since 1940 through the 1970s.
Using green plants to clean up contaminated soil groundwater and wastewater.