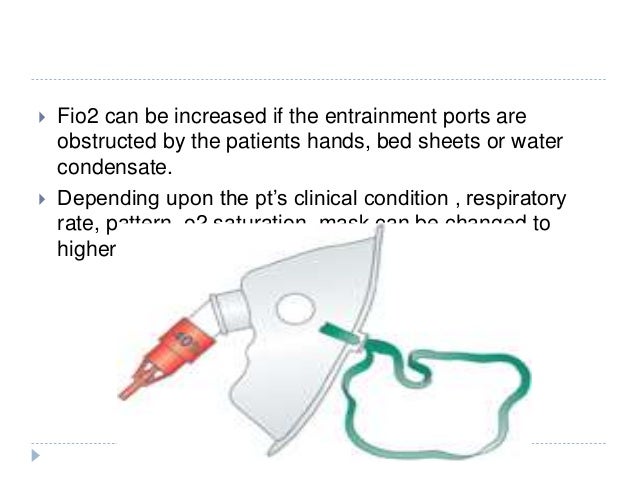
Documented hypoxemia in adults children and infants older than 28 days arterial oxygen tension pao2 of 60 mmhg or arterial oxygen saturation sao2 of 90 in subjects breathing room air or with pao2 and or sao2 below desirable range for specific clinical situation in neonates pao2 50.
Pediatric oxygen delivery devices ppt.
Child s size and tidal volume alter the oxygen concentration child receives despite same flow rate.
Provide a constant fio2 by delivering the gas at flow rates that exceed the patient s peak inspiratory flow rate and by using devices that entrain a.
Selection of an oxygen delivery device for neonatal and pediatric patients 2002 revision update.
Aarc clinical practice guideline.
Long term oxygen therapy has been shown to improve survival and decrease the hospitalization rates in patients with copd.
Inadequate oxygen delivery and vice versa.
Reduce the work of breathing.
Indications for oxygen use low ambient o2 hypoxemia suspected hypoxemia increased work of breathing flaring tachypnea increased myocardial work acute head injury o2 delivery systems high flow venti masks air entrainment masks mechanical aerosol systems high flow humidifier systems low flow nasal cannula simple masks partial rebreathing masks non rebreathing masks entrainment ratios delivered.
Myers tr american association for respiratory care aarc.
Milross j young ih donnelly p.
Withholding oxygen can have a detrimental effect yet continuing to provide oxygen therapy when it is no longer indicated can prolong hospitalization and increase the cost of care.
This comprehensive review begins with an assessment of need and a review of physiologic effects potential toxicities and common delivery devices and it ends with advances in oxygen therapy with a focus on the.
Give oxygen therapy in a way which prevents excessive co 2 accumulation i e.
84 this type of oxygen delivery device is composed of traditional nasal.
Pulse dose oxygen delivery devices and demand oxygen delivery systems have been shown to be effective in resting exercising and sleeping patients.
Oxygen delivery devices 1.
Selection of the appropriate flow rate and delivery device.
Other factors that complicate achievement of oxygen therapy goals include pa tient size and tolerance of delivery devices.
Provide oxygen at flow rates that are lower than patients inspiratory demands when the total ventilation exceeds the capacity of the oxygen reservoir room air is entrained 2 high flow devices.
Performance characteristics may vary.
Variability in the use of delivery devices suggesting that clinicians often lack adequate knowledge in the use of oxygen delivery equip.
Blenders may be used to wean oxygen titration of flow rates.
Oxygen delivery devices dr.
The oxygen delivery characteristics of the hudson oxy one face mask.
Ensure adequate clearance of secretions and limit the adverse events of hypothermia and insensible water loss by use of optimal humidification dependent on mode of oxygen delivery.
Most commonly used oxygen delivery device.
Maximum oxygen flow should not exceed 4 l min.